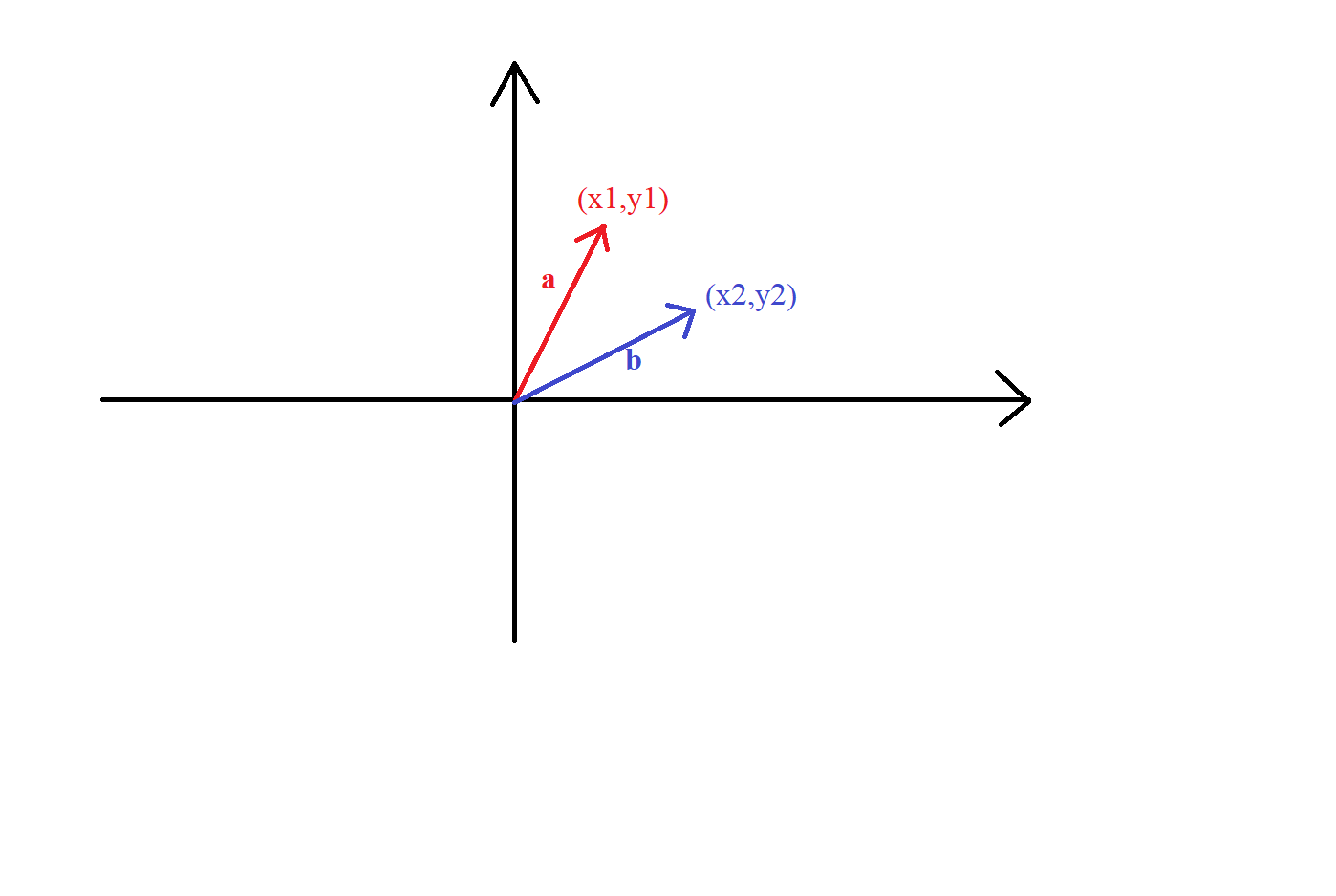
首先介绍一下向量叉积的定义:
对于向量a ⃗ ( x 1 , y 1 ) \vec a (x_1,y_1) a ( x 1 , y 1 ) b ⃗ ( x 2 , y 2 ) \vec b (x_2,y_2) b ( x 2 , y 2 )
向量的叉积a ⃗ × b ⃗ \vec a \times \vec b a × b x 1 × y 2 − y 1 × x 2 x_1 \times y_2 - y_1 \times x_2 x 1 × y 2 − y 1 × x 2
代码如下:
1 2 3 inline double operator * (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x; }
考虑有什么几何意义
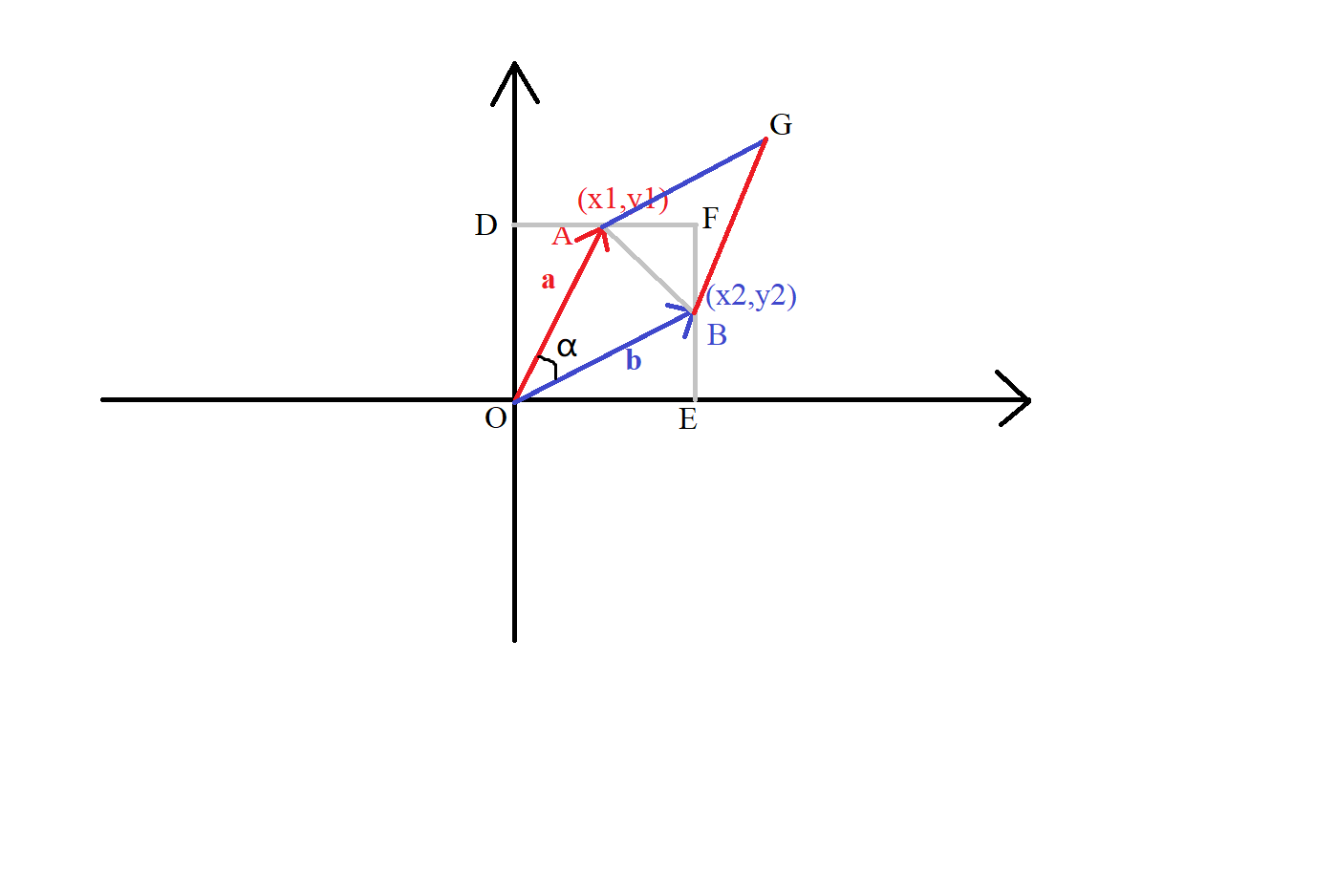
把a ⃗ \vec a a b ⃗ \vec b b
考虑S Δ O A B S_{\Delta OAB} S Δ O A B
用初中的方法推一下:
S Δ O A B = S O E F D − S Δ A B F − S Δ O A D − S Δ O B E S_{\Delta OAB}=S_{OEFD}-S_{\Delta ABF}-S_{\Delta OAD}-S_{\Delta OBE} S Δ O A B = S O E F D − S Δ A B F − S Δ O A D − S Δ O B E
= ( x 2 × y 1 ) − ( x 2 − x 1 ) × ( y 1 − y 2 ) / 2 − x 2 × y 2 / 2 − x 1 × y 1 / 2 =(x_2 \times y_1)-(x_2-x_1) \times (y_1 -y_2)/2-x_2 \times y_2 /2 -x_1 \times y_1 /2 = ( x 2 × y 1 ) − ( x 2 − x 1 ) × ( y 1 − y 2 ) / 2 − x 2 × y 2 / 2 − x 1 × y 1 / 2
= ( x 1 × y 2 − y 1 × x 2 ) / 2 =(x_1 \times y_2-y_1 \times x_2)/2 = ( x 1 × y 2 − y 1 × x 2 ) / 2
对于其他a ⃗ \vec a a b ⃗ \vec b b x 1 × y 2 − y 1 × x 2 x_1 \times y_2-y_1 \times x_2 x 1 × y 2 − y 1 × x 2 0 0 0
于是S Δ O A B = ∣ a ⃗ × b ⃗ / 2 ∣ S_{\Delta OAB} = |\vec a\times \vec b/2| S Δ O A B = ∣ a × b / 2 ∣
于是S O A B G = ∣ a ⃗ × b ⃗ ∣ S_{OABG}=|\vec a \times \vec b| S O A B G = ∣ a × b ∣
其他方法如割补法也是可以得到这个结论的。
于是向量叉积的几何意义就是两个向量形成的平行四边形的面积
继续推一下,我们有三角函数公式S Δ O A B = sin α × O A × O B / 2 S_{\Delta OAB}=\sin α \times OA \times OB/2 S Δ O A B = sin α × O A × O B / 2
所以a ⃗ × b ⃗ = ∣ a ⃗ ∣ × ∣ b ⃗ ∣ × sin ∠ A O B \vec a \times \vec b = |\vec a| \times |\vec b| \times \sin ∠AOB a × b = ∣ a ∣ × ∣ b ∣ × sin ∠ A O B
其中∣ a ⃗ ∣ |\vec a| ∣ a ∣ a . x 2 + a . y 2 \sqrt{a.x^2+a.y^2} a . x 2 + a . y 2
观察到a ⃗ \vec a a b ⃗ \vec b b ∠ A O B ∠AOB ∠ A O B sin ∠ A O B \sin ∠AOB sin ∠ A O B 0 0 0 a ⃗ × b ⃗ < 0 \vec a \times \vec b <0 a × b < 0
于是我们又有一个重要的结论,当a ⃗ \vec a a b ⃗ \vec b b a ⃗ × b ⃗ < 0 \vec a \times \vec b<0 a × b < 0
好了,数学部分大部分推完了,讲一讲凸包的定义:
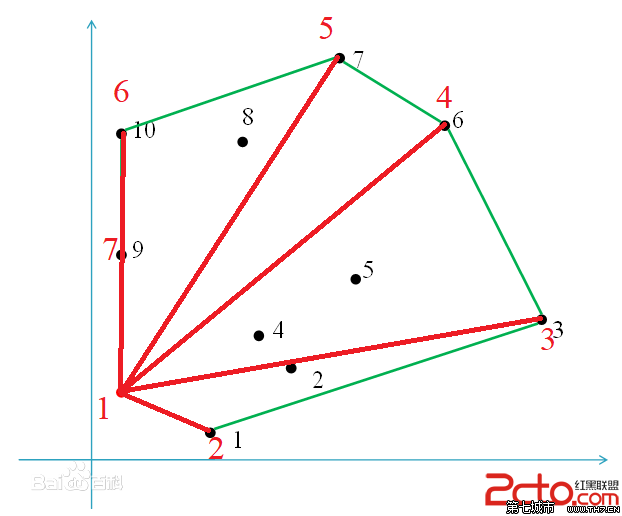
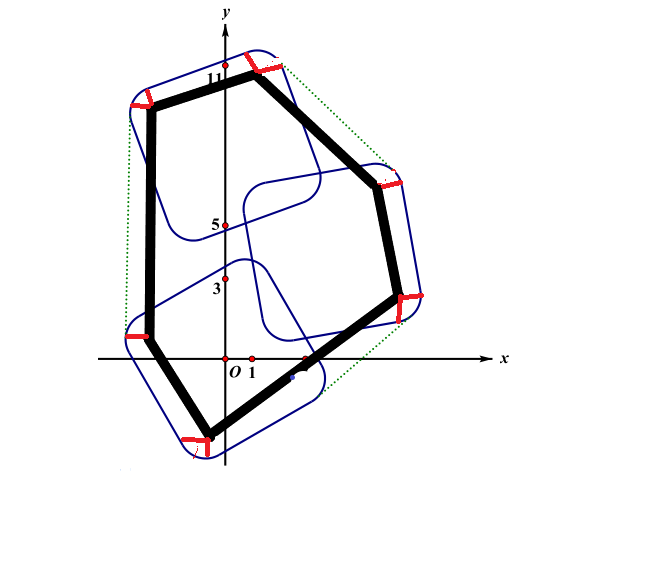
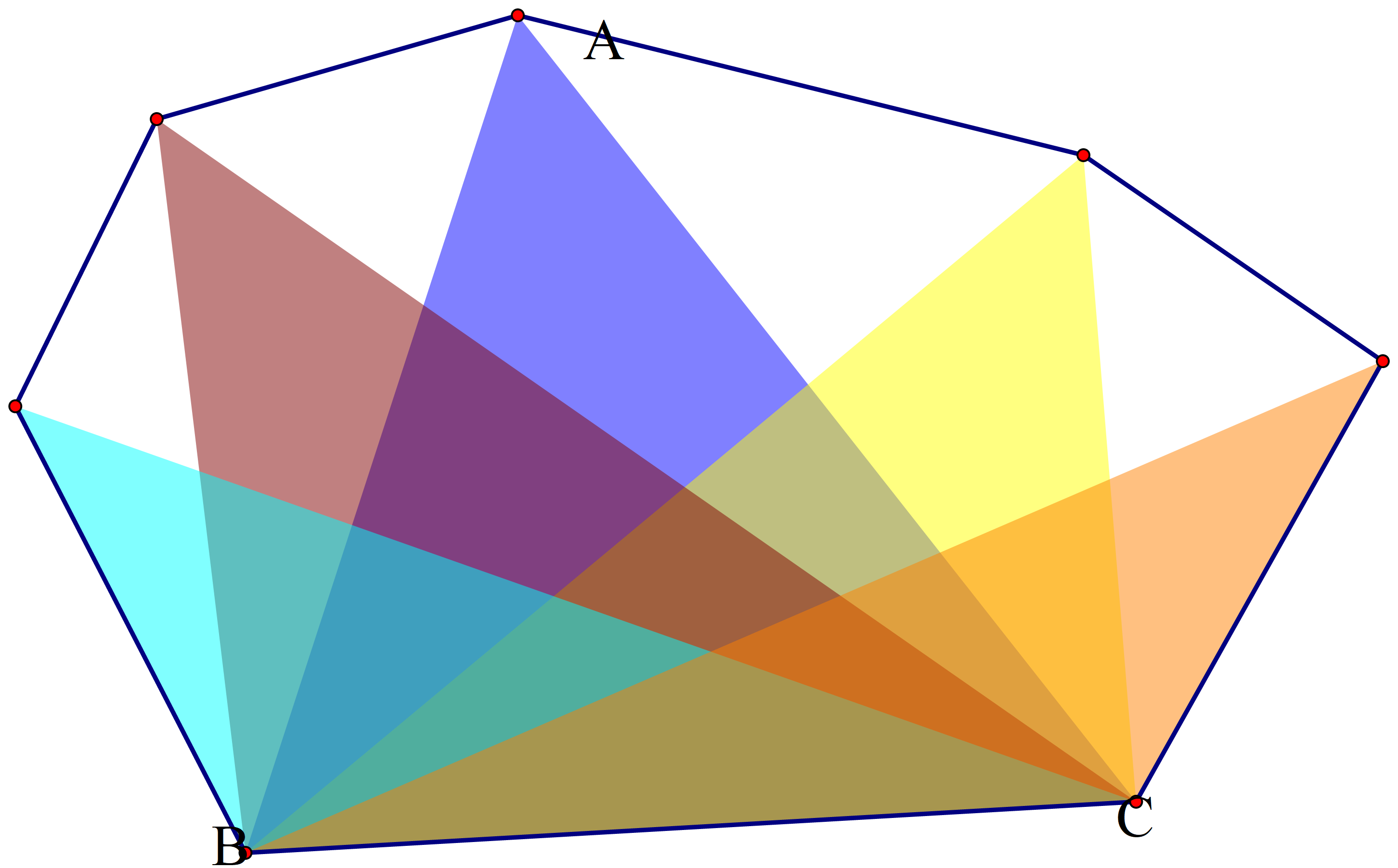
给定二维平面上的点集,凸包就是将最外层的点连接起来构成的凸多边形,它能包含点集中所有的点
(对于图中9 9 9
如何快速求出凸包,考虑一个重要的性质:
考虑以上图中的红色点为基准点,重新建立直角坐标系,发现凸包任意两个点中,编号较大的点对应的向量总是在编号较小的点对应的向量的逆时针方向,于是他们俩叉积大于0 0 0
于是对于建立凸包,我们有一个重要的思路,考虑钦定一个点a a a x x x y y y A , B A,B A , B = 0 =0 = 0
1 2 3 4 inline bool operator < (const Point &A,const Point &B){ if (((A-a)*(B-a))!=0 ) return ((A-a)*(B-a))>0 ; else return dis (a,A)<dis (a,B); }
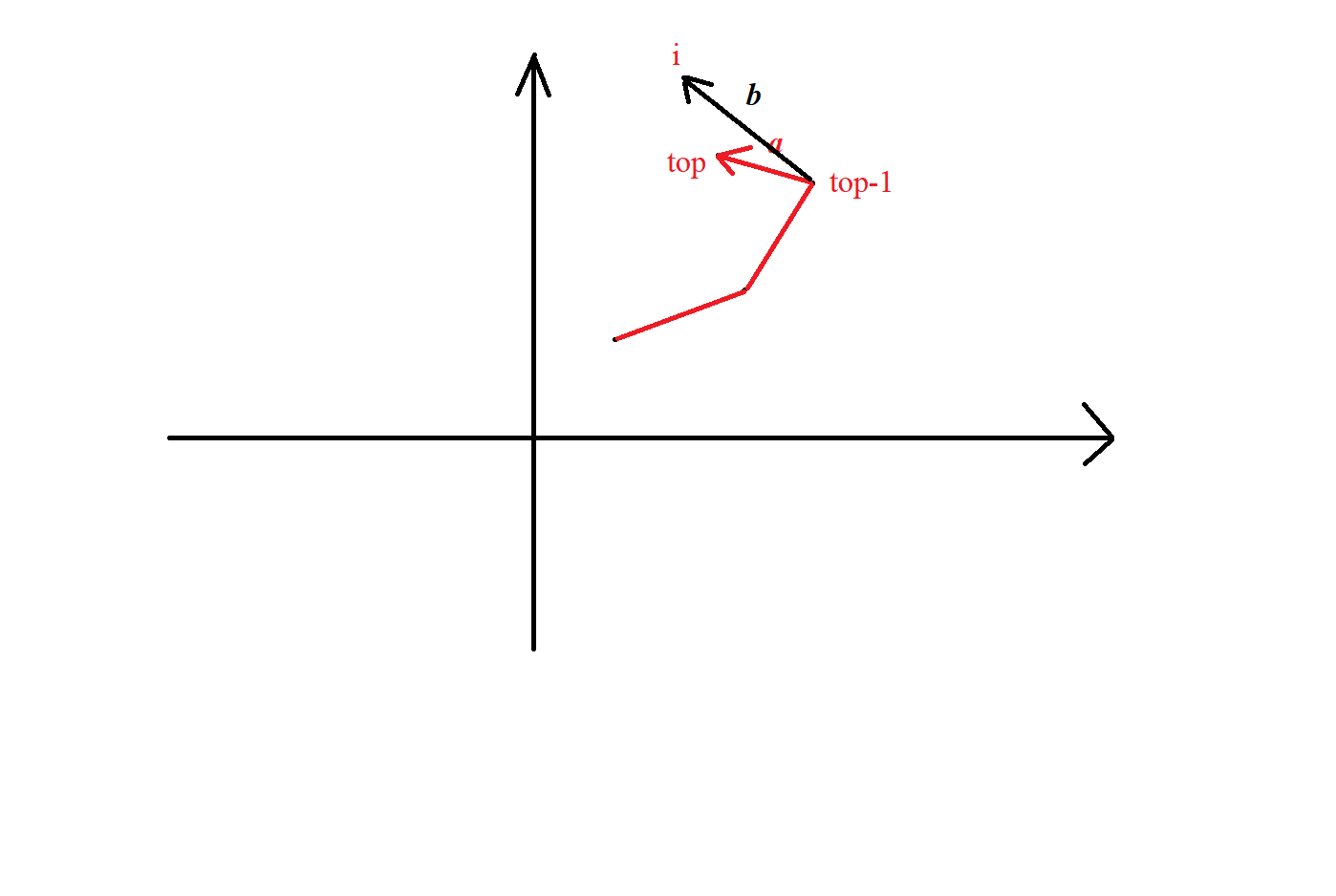
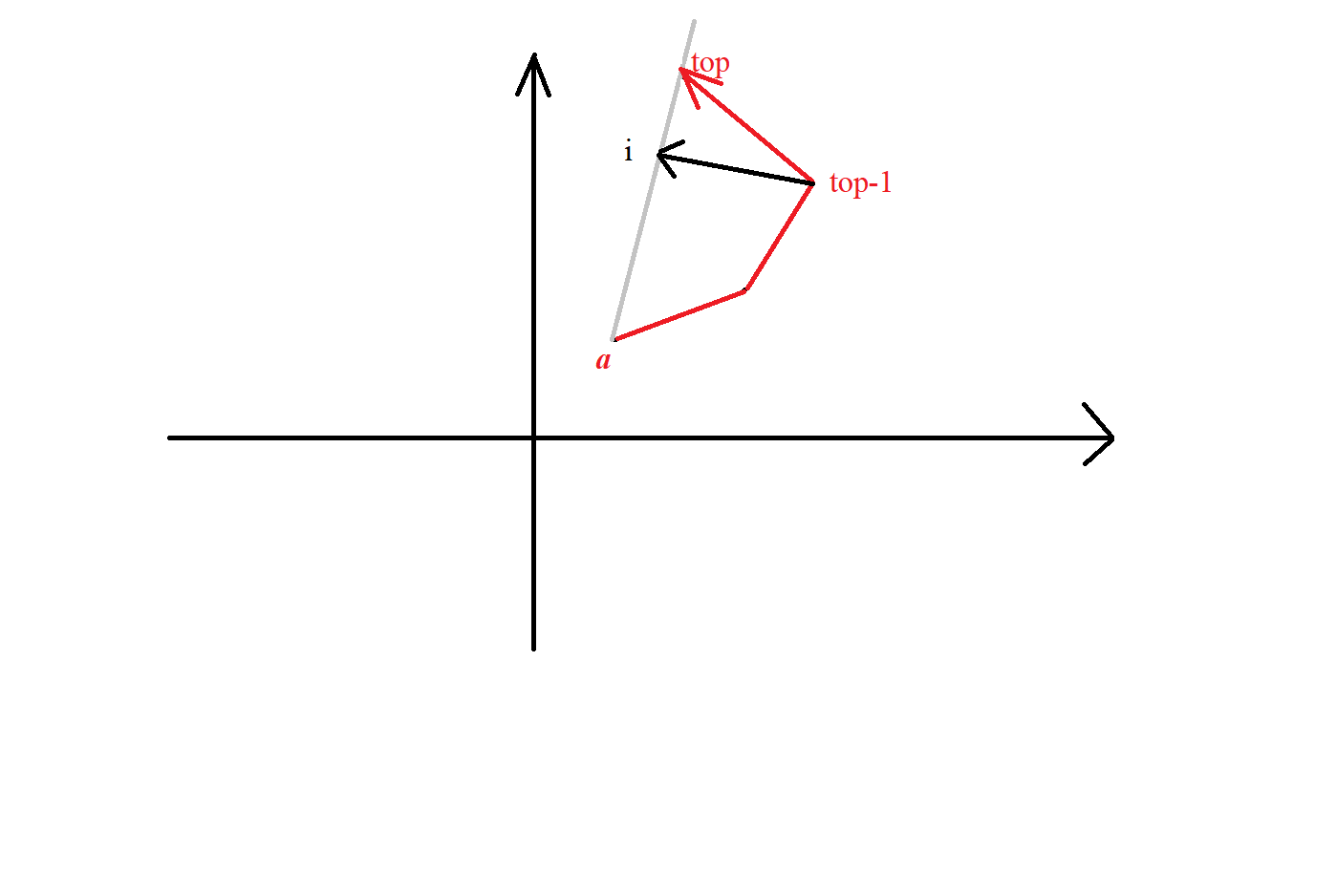
考虑现在已经建出的凸包(红色部分),我们用一个单调栈来存凸包上面的点,假设我们要加进一个点i i i a ⃗ \vec a a b ⃗ \vec b b a ⃗ \vec a a b ⃗ \vec b b a ⃗ × b ⃗ < 0 \vec a \times \vec b <0 a × b < 0 i , t o p , t o p − 1 i,top ,top-1 i , t o p , t o p − 1
1 2 3 4 5 sort (p+2 ,p+1 +n);for (register int i=1 ;i<=n;++i){ while (top>1 &&(stk[top]-stk[top-1 ])*(p[i]-stk[top-1 ])<=0 ) top--; stk[++top]=p[i]; }
为什么排序要加和基准点距离的特判,考虑如图的情况,如果t o p top t o p i i i t o p top t o p i i i
护城河的挖掘/P2742 【模板】二维凸包 / [USACO5.1]圈奶牛Fencing the Cows
传送门
求凸包周长,很简单,只要把凸包里面相邻两点的距离算一下相加即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define MAXN 100005 using namespace std;struct Point { double x,y; }p[MAXN]; Point a; int pos;inline double operator * (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x; } inline Point operator - (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return Point{A.x-B.x,A.y-B.y}; } inline double pf (double x) return x*x; } inline double dis (const Point &A,const Point &B) return sqrt (pf (A.x-B.x)+pf (A.y-B.y)); } inline bool operator < (const Point &A,const Point &B){ if (((A-a)*(B-a))!=0 ) return ((A-a)*(B-a))>0 ; else return dis (a,A)<dis (a,B); } Point stk[MAXN]; int top;int main () int n; scanf ("%d" ,&n); pos=1 ; for (register int i=1 ;i<=n;++i){ double x,y; scanf ("%lf%lf" ,&x,&y); p[i].x=(double )(x),p[i].y=(double )(y); if (p[pos].y>p[i].y||(p[pos].y==p[i].y&&p[pos].x>p[i].x)) pos=i; } a=p[pos]; swap (p[1 ],p[pos]); sort (p+2 ,p+1 +n); for (register int i=1 ;i<=n;++i){ while (top>1 &&(stk[top]-stk[top-1 ])*(p[i]-stk[top-1 ])<=0 ) top--; stk[++top]=p[i]; } double ans=0 ; for (register int i=1 ;i<top;++i){ ans+=dis (stk[i],stk[i+1 ]); } ans+=dis (stk[top],stk[1 ]); printf ("%.2f\n" ,ans); }
P3829 [SHOI2012]信用卡凸包
图是洛谷上面剽的。
考虑把每个信用卡的四个圆弧对应的圆心找出来跑凸包,凸包的周长加上一个整圆的周长即是答案,为什么?
考虑把凸包上面的边平移进去,发现红色的几段圆弧刚好能拼成一个大圆,所以得证。
具体实现的时候,可以使用公式旋转向量:
1 2 3 inline Point Rotate (Point a,double theta) return Point{a.x*cos (theta)-a.y*sin (theta),a.x*sin (theta)+a.y*cos (theta)}; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #include <cmath> #define MAXN 1000005 #define eps 1e-10 using namespace std;struct Point { double x,y; }p[MAXN]; Point p0; int pos;inline double operator * (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x; } inline Point operator - (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return Point{A.x-B.x,A.y-B.y}; } inline Point operator + (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return Point{A.x+B.x,A.y+B.y}; } inline double pf (double x) return x*x; } inline double dis (const Point &A,const Point &B) return sqrt (pf (A.x-B.x)+pf (A.y-B.y)); } inline bool operator < (const Point &A,const Point &B){ if (abs ((A-p0)*(B-p0))>eps) return ((A-p0)*(B-p0))>eps; else return dis (p0,A)<dis (p0,B); } Point stk[MAXN]; int top,cnt;inline void Insert (Point a) p[++cnt]=a; if (p[pos].y>p[cnt].y||(p[pos].y==p[cnt].y&&p[pos].x>p[cnt].x)) pos=cnt; } inline Point Rotate (Point a,double theta) return Point{a.x*cos (theta)-a.y*sin (theta),a.x*sin (theta)+a.y*cos (theta)}; } Point d[4 ]; double fh[2 ]={1.00 ,-1.00 };int main () int n; scanf ("%d" ,&n); double a,b,R; cin>>a>>b>>R; swap (a,b); a-=2.00 *R,b-=2.00 *R; for (register int i=0 ;i<2 ;++i){ for (register int j=0 ;j<2 ;++j){ d[i*2 +j]=Point{fh[i]*a/2.00 ,fh[j]*b/2.00 }; } } pos=1 ; for (register int i=1 ;i<=n;++i){ double r,x,y; cin>>x>>y>>r; Point A=Point{x,y}; for (register int j=0 ;j<4 ;++j){ Insert (A+Rotate (d[j],r)); } } p0=p[pos]; swap (p[1 ],p[pos]); sort (p+2 ,p+1 +cnt); for (register int i=1 ;i<=cnt;++i){ while (top>1 &&(stk[top]-stk[top-1 ])*(p[i]-stk[top-1 ])<=-eps) top--; stk[++top]=p[i]; } double ans=0 ; for (register int i=1 ;i<top;++i){ ans+=dis (stk[i],stk[i+1 ]); } ans+=dis (stk[top],stk[1 ]); ans+=2.00 *acos (-1 )*R; printf ("%.2lf\n" ,ans); }
[HAOI2011]防线修建
首先,我们将删点变成加点,就是把删点的操作离线下来,反向操作。
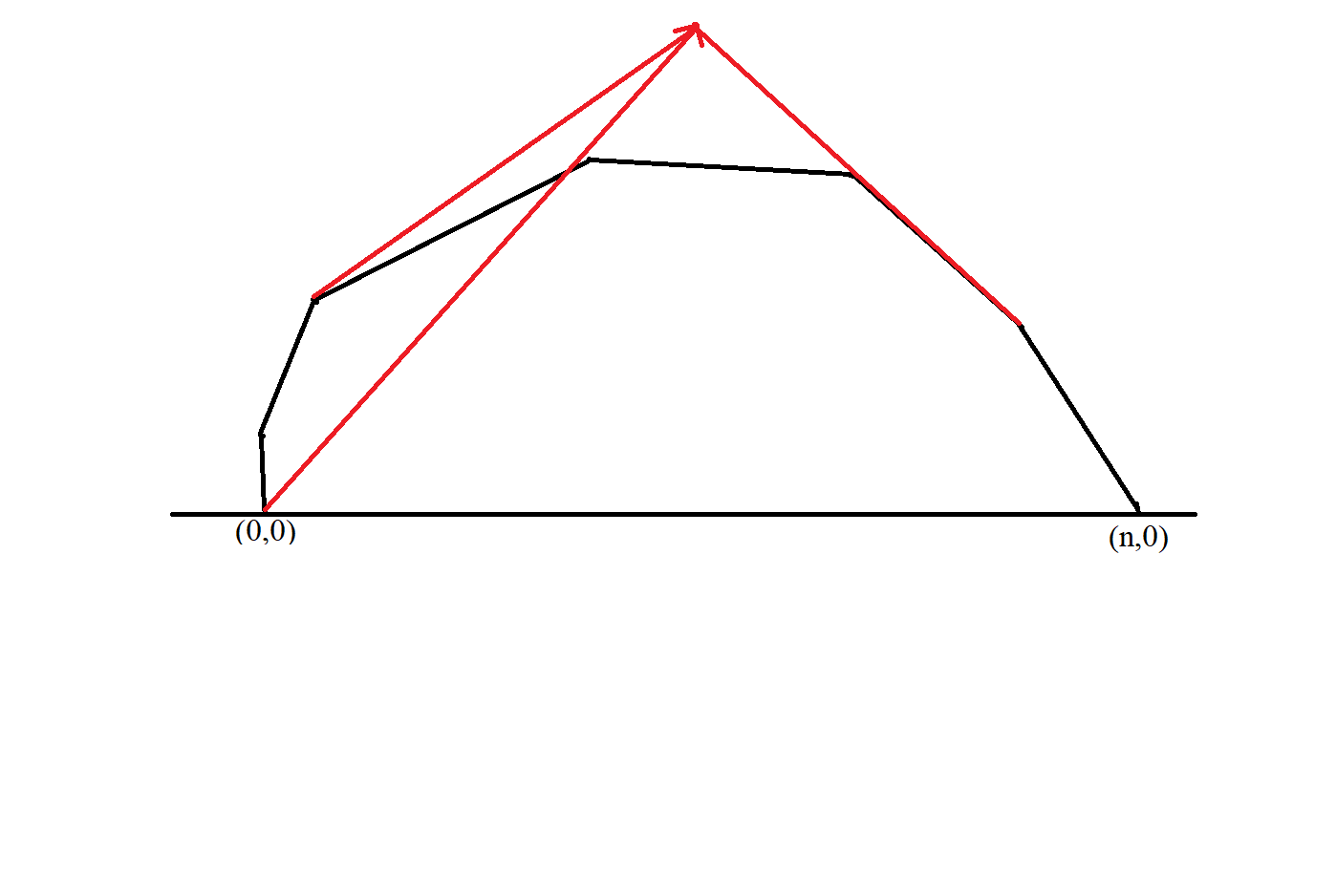
于是题目就是要你动态维护一个上凸壳的周长。
考虑s e t set s e t s e t set s e t x , y x,y x , y
1 if ((*r-*l)*(x-*l)<0 ) return ;
如果不在凸包里面,就得把不符合凸包性质的点一个一个删掉,由于总共的点数为n n n O ( log n ) O(\log n) O ( log n )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 while (true ){ t=r;r++; if (r==S.end ()) break ; if ((*r-x)*(*t-x)>0 ) break ; ans-=dis (*t,*r); S.erase (*t); } while (l!=S.begin ()){ t=l;l--; if ((*t-x)*(*l-x)>0 ) break ; ans-=dis (*t,*l); S.erase (*t); } S.insert (x); r=S.lower_bound (x),l=r; l--,r++; ans+=dis (x,*l)+dis (x,*r);
别忘了加上红色的两条边。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #include <cmath> #define MAXN 1000005 #define eps 1e-6 using namespace std;struct Point { double x,y; }p[MAXN]; Point p0; int pos;inline double operator * (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x; } inline Point operator - (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return Point{A.x-B.x,A.y-B.y}; } inline Point operator + (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return Point{A.x+B.x,A.y+B.y}; } inline double pf (double x) return x*x; } inline double dis (const Point &A,const Point &B) return sqrt (pf (A.x-B.x)+pf (A.y-B.y)); } bool flag;inline bool operator < (const Point &A,const Point &B){ if (flag){ if (abs ((A-p0)*(B-p0))>eps) return ((A-p0)*(B-p0))>eps; else return dis (p0,A)<dis (p0,B); } else { if (A.x!=B.x) return A.x<B.x; else return A.y>B.y; } } Point stk[MAXN]; int top,cnt;inline void Insert (Point a) p[++cnt]=a; if (p[pos].y>p[cnt].y||(p[pos].y==p[cnt].y&&p[pos].x>p[cnt].x)) pos=cnt; } set<Point>S; int vis[MAXN],id[MAXN],tot;Point c[MAXN]; double ans;inline void Add (Point a) c[++tot]=a; } inline void Init () pos=1 ; cnt=0 ; for (register int i=1 ;i<=tot;++i){ if (!vis[i]) Insert (c[i]); } p0=p[pos]; swap (p[1 ],p[pos]); flag=true ; sort (p+2 ,p+1 +cnt); flag=false ; for (register int i=1 ;i<=cnt;++i){ while (top>1 &&(stk[top]-stk[top-1 ])*(p[i]-stk[top-1 ])<=0 ) top--; stk[++top]=p[i]; } ans=0 ; for (register int i=2 ;i<top;++i){ ans+=dis (stk[i],stk[i+1 ]); } ans+=dis (stk[top],stk[1 ]); S.clear (); for (register int i=1 ;i<=top;++i){ S.insert (stk[i]); } } inline void Print () printf ("Set Elements:\n" ); for (set<Point>::iterator it=S.begin ();it!=S.end ();++it){ printf ("%f %f\n" ,(*it).x,(*it).y); } printf ("\n" ); } inline void AddCity (Point x) set<Point>::iterator r=S.lower_bound (x),l=r,t; l--; if ((*r-*l)*(x-*l)<0 ) return ; ans-=dis (*l,*r); S.insert (x); while (true ){ t=r;r++; if (r==S.end ()) break ; if ((*r-x)*(*t-x)>0 ) break ; ans-=dis (*t,*r); S.erase (*t); } while (l!=S.begin ()){ t=l;l--; if ((*t-x)*(*l-x)>0 ) break ; ans-=dis (*t,*l); S.erase (*t); } S.insert (x); r=S.lower_bound (x),l=r; l--,r++; ans+=dis (x,*l)+dis (x,*r); } double Ans[MAXN];int n,sx,sy,m;int main () scanf ("%d%d%d" ,&n,&sx,&sy); Add (Point{(double )sx,(double )sy}); scanf ("%d" ,&m); for (register int i=1 ;i<=m;++i){ int x,y; scanf ("%d%d" ,&x,&y); Add (Point{(double )x,(double )y}); } Add (Point{0 ,0 }); Add (Point{(double )n,0 }); int q; scanf ("%d" ,&q); for (register int i=1 ;i<=q;++i){ int opr; scanf ("%d" ,&opr); if (opr==1 ){ int city; scanf ("%d" ,&city); vis[city+1 ]=1 ; id[i]=city+1 ; } else { id[i]=0 ; } } Init (); for (register int i=q;i>=1 ;--i){ if (id[i]) AddCity (c[id[i]]); else Ans[i]=ans; } for (register int i=1 ;i<=q;++i){ if (!id[i]){ printf ("%.2f\n" ,Ans[i]); } } }
P1452 Beauty Contest
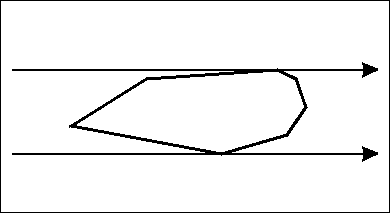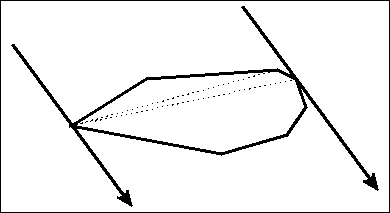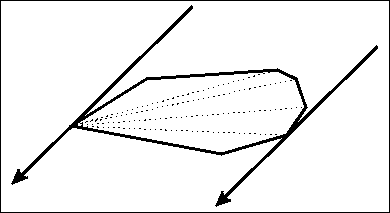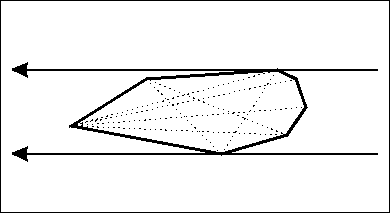
让你求一个凸包的直径。
考虑到点数很多,但是凸包上面的点很少,所以可以用暴力水过:
1 2 3 4 5 6 double ans=0 ;for (register int i=1 ;i<=top;++i){ for (register int j=i+1 ;j<=top;++j){ ans=max (ans,dis (stk[i],stk[j])*dis (stk[i],stk[j])); } }
考虑如何做到O ( n ) O(n) O ( n )
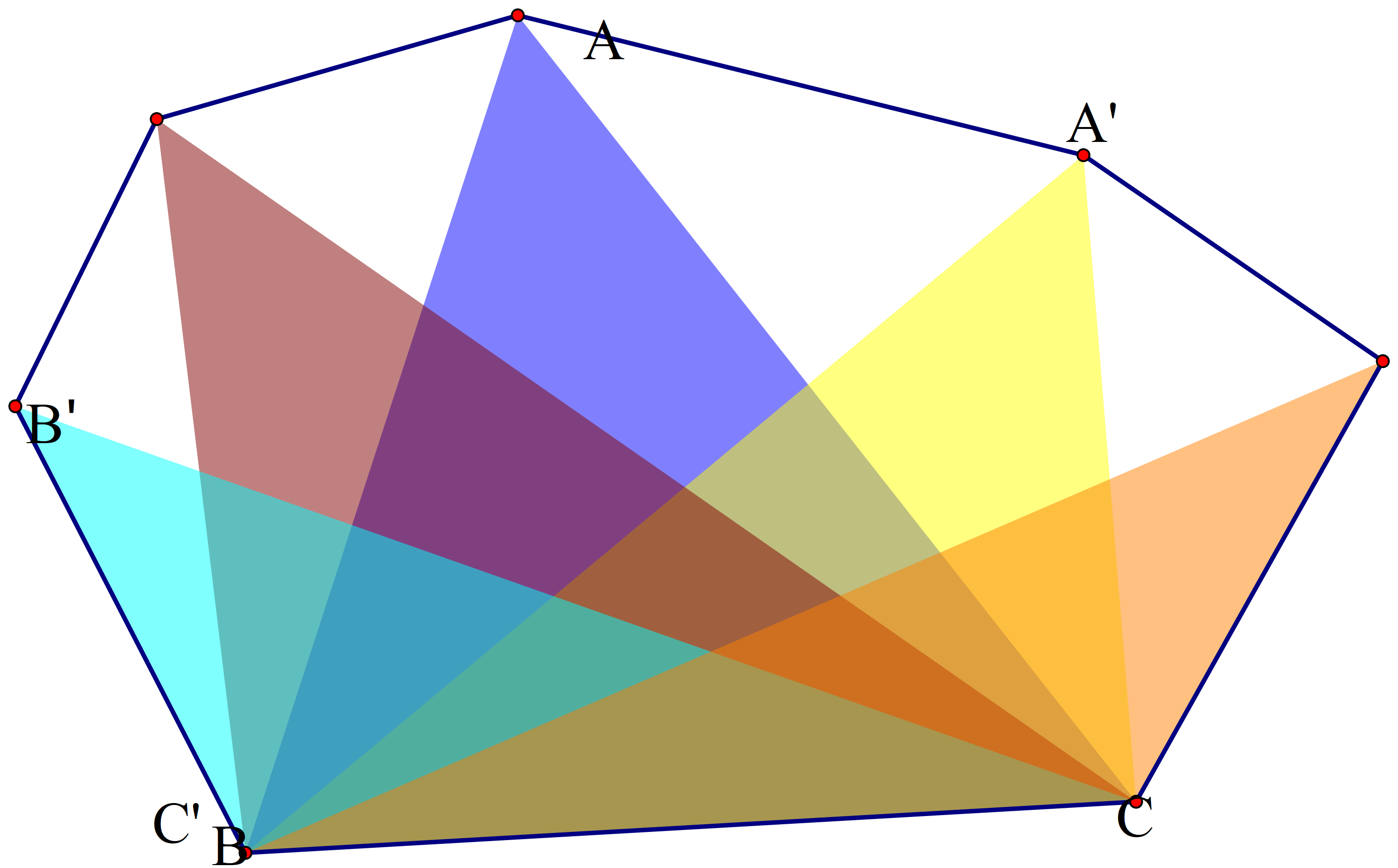
我们使用旋转卡壳算法,放一个图直观感受一下:
定义对踵点为一条边和凸包上面其他点形成的三角形中面积最大的一个的顶点,如图中B C BC B C A A A
考虑将B C BC B C B ′ C ′ B'C' B ′ C ′ A A A
于是A A A O ( n ) O(n) O ( n ) A A A
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 register int ptr=2 ;stk[top+1 ]=stk[1 ]; for (register int i=1 ;i<=top;++i){ while (Height (stk[ptr]-stk[i],stk[ptr]-stk[i+1 ])<Height (stk[ptr+1 ]-stk[i],stk[ptr+1 ]-stk[i+1 ])){ ptr++; if (ptr==top+1 ) ptr=1 ; } ans=max (ans,dis (stk[i],stk[ptr])*dis (stk[i],stk[ptr])); }
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #include <cmath> #define MAXN 500005 #define eps 1e-10 using namespace std;struct Point { double x,y; }p[MAXN]; Point p0; int pos;inline double operator * (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x; } inline Point operator - (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return Point{A.x-B.x,A.y-B.y}; } inline Point operator + (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return Point{A.x+B.x,A.y+B.y}; } inline double pf (double x) return x*x; } inline double dis (const Point &A,const Point &B) return sqrt (pf (A.x-B.x)+pf (A.y-B.y)); } inline bool operator < (const Point &A,const Point &B){ if (abs ((A-p0)*(B-p0))>eps) return ((A-p0)*(B-p0))>eps; else return dis (p0,A)<dis (p0,B); } Point stk[MAXN]; int top,cnt;inline void Insert (Point a) p[++cnt]=a; if (p[pos].y>p[cnt].y||(p[pos].y==p[cnt].y&&p[pos].x>p[cnt].x)) pos=cnt; } inline double Height (Point a,Point b) return (a*b)/dis (a,b); } int main () int n; scanf ("%d" ,&n); pos=1 ; for (register int i=1 ;i<=n;++i){ double x,y; cin>>x>>y; Insert (Point{x,y}); } p0=p[pos]; swap (p[1 ],p[pos]); sort (p+2 ,p+1 +cnt); for (register int i=1 ;i<=cnt;++i){ while (top>1 &&(stk[top]-stk[top-1 ])*(p[i]-stk[top-1 ])<=0 ) top--; stk[++top]=p[i]; } double ans=0 ; register int ptr=2 ; stk[top+1 ]=stk[1 ]; for (register int i=1 ;i<=top;++i){ while (Height (stk[ptr]-stk[i],stk[ptr]-stk[i+1 ])<Height (stk[ptr+1 ]-stk[i],stk[ptr+1 ]-stk[i+1 ])){ ptr++; if (ptr==top+1 ) ptr=1 ; } ans=max (ans,dis (stk[i],stk[ptr])*dis (stk[i],stk[ptr])); } printf ("%.0f\n" ,ans); }
P3187 [HNOI2007]最小矩形覆盖
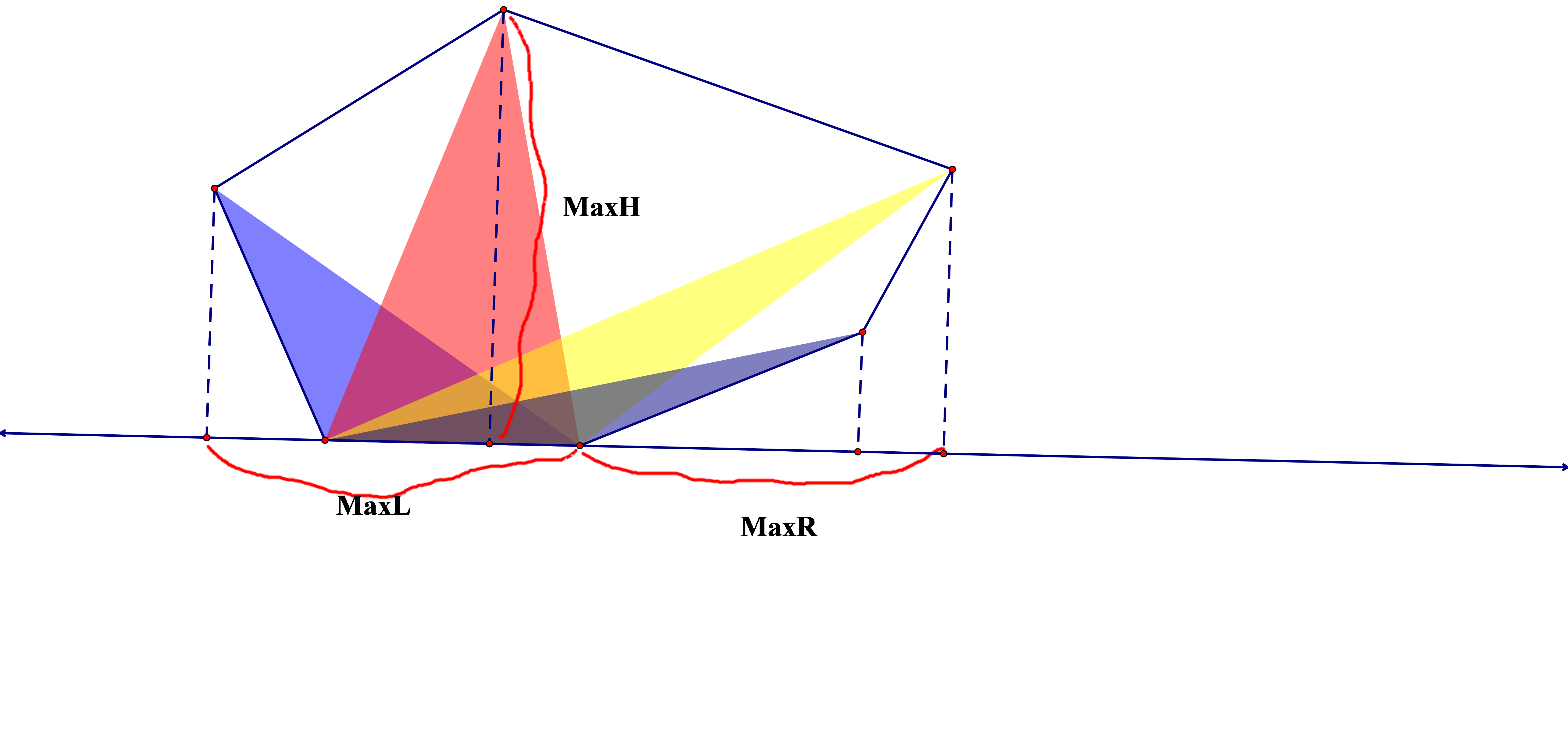
给定一些点的坐标,要求求能够覆盖所有点的最小面积的矩形,输出所求矩形的面积和四个顶点坐标。
首先考虑建出凸包,发现这个矩形的一条边一定在凸包上面,考虑枚举这条边,发现最小矩形的长为M a x L + M a x R MaxL+MaxR M a x L + M a x R M a x H MaxH M a x H
于是考虑旋转卡壳求出M a x H MaxH M a x H M a x L , M a x R MaxL,MaxR M a x L , M a x R M a x H MaxH M a x H M a x L , M a x R MaxL,MaxR M a x L , M a x R
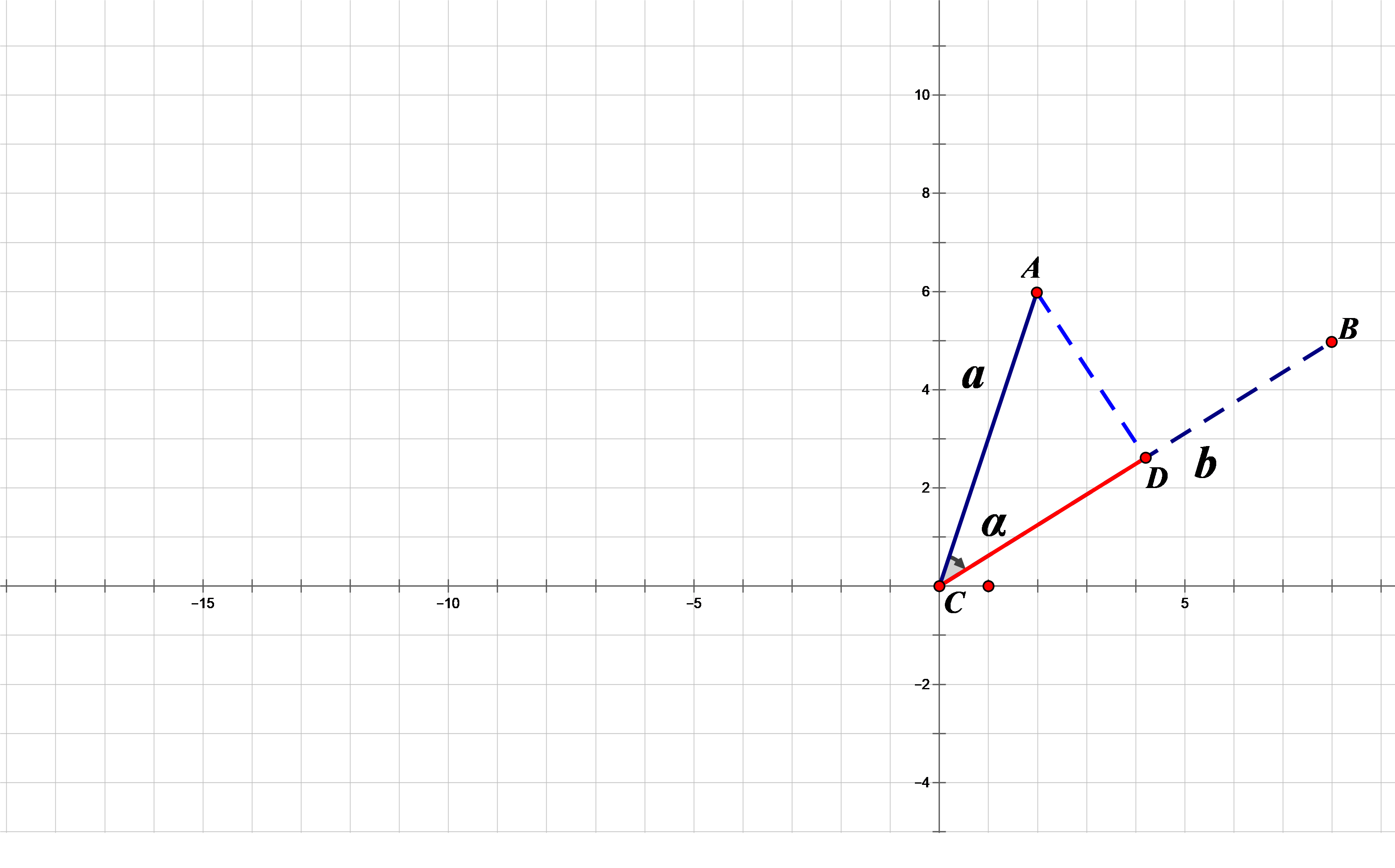
再介绍向量的点积,
对于向量a ⃗ ( x 1 , y 1 ) \vec a (x_1,y_1) a ( x 1 , y 1 ) b ⃗ ( x 2 , y 2 ) \vec b (x_2,y_2) b ( x 2 , y 2 )
向量的点积a ⃗ ⋅ b ⃗ \vec a · \vec b a ⋅ b x 1 × y 1 − x 2 × y 2 x_1 \times y_1 - x_2 \times y_2 x 1 × y 1 − x 2 × y 2
也可以表示为∣ a ⃗ ∣ × ∣ b ⃗ ∣ × cos α |\vec a| \times |\vec b| \times \cos \alpha ∣ a ∣ × ∣ b ∣ × cos α
注意到∣ a ⃗ ∣ × cos α |\vec a| \times \cos \alpha ∣ a ∣ × cos α a ⃗ \vec a a b ⃗ \vec b b
所以我们有C D = a ⃗ ⋅ b ⃗ / ∣ b ⃗ ∣ CD=\vec a · \vec b / |\vec b| C D = a ⋅ b / ∣ b ∣
回到本题,发现M a x L MaxL M a x L M a x R MaxR M a x R
1 2 double L=abs ((stk[l]-stk[i])^(stk[i]-stk[i+1 ]))/D;double R=abs ((stk[r]-stk[i])^(stk[i]-stk[i+1 ]))/D;
求得M a x L , M a x R , M a x H MaxL,MaxR,MaxH M a x L , M a x R , M a x H
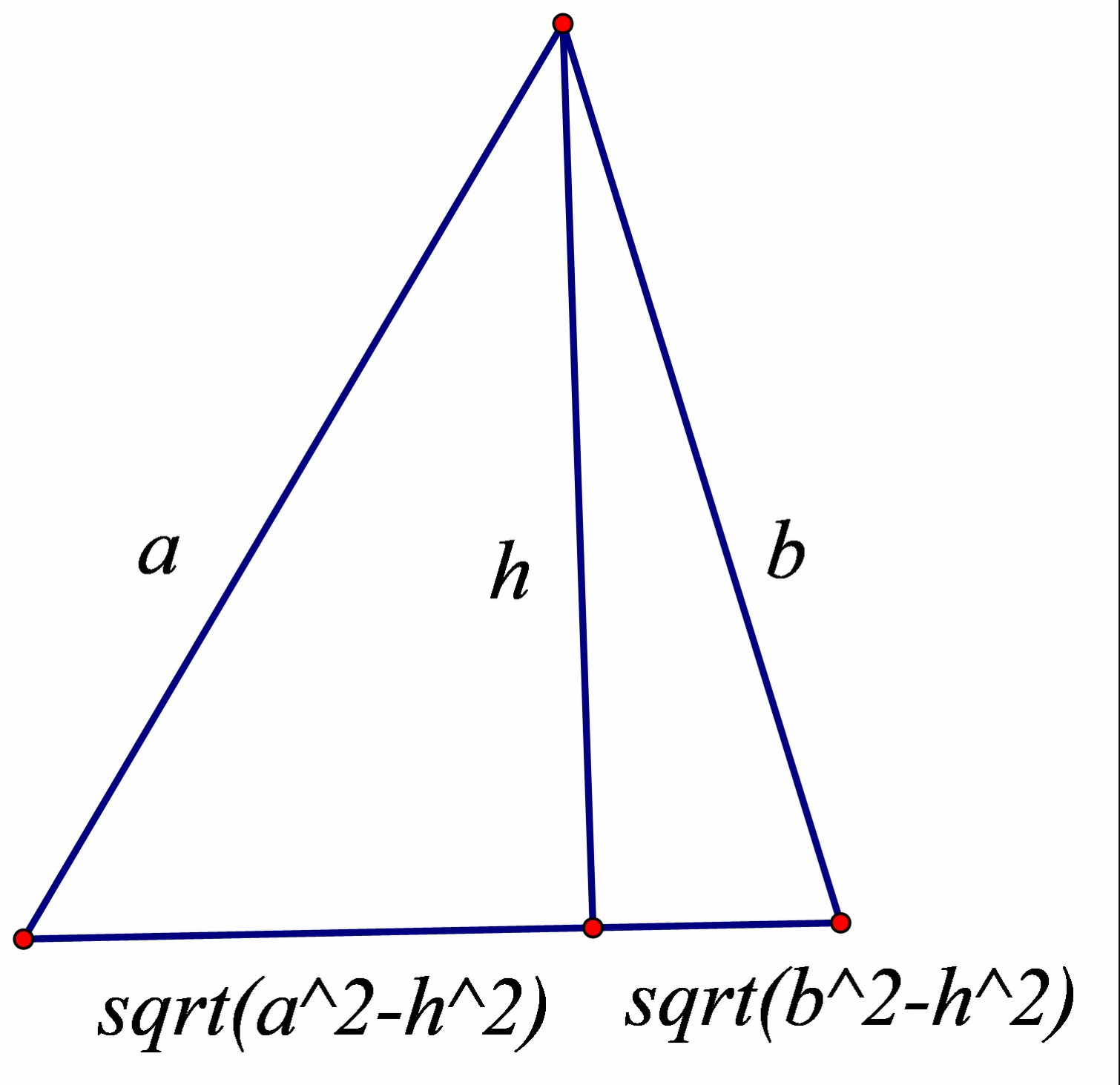
我们知道向量a ⃗ \vec a a b ⃗ \vec b b h ⃗ \vec h h
1 2 3 4 Point a=stk[i]-stk[h],b=stk[i+1 ]-stk[h]; double aa=mod (a),bb=mod (b);double x=sqrt (abs (aa-H*H)),y=sqrt (abs (bb-H*H));Point hh=(mul (a,y)+mul (b,x))/(x+y);
交上去被卡精度怎么办,发现数据都是整数,于是四舍五入到整数
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define MAXN 50005 #define eps std::numeric_limits<double> ::epsilon() * 10 #define EPS 0.7 using namespace std;inline void PrintDouble (double x) printf ("%.5lf" ,(double ((int )(x+EPS)*100000 )/100000 )); } struct Point { double x,y; void print () PrintDouble (x); printf (" " ); PrintDouble (y); printf ("\n" ); } }p[MAXN]; Point p0; int pos;inline double operator * (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x; } inline Point operator - (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return Point{A.x-B.x,A.y-B.y}; } inline Point operator + (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return Point{A.x+B.x,A.y+B.y}; } inline double operator ^ (const Point &A,const Point &B){ return A.x*B.x+A.y*B.y; } inline Point operator / (const Point &A,const double &D){ return Point{A.x/D,A.y/D}; } inline Point mul (const Point &A,const double &D) return Point{A.x*D,A.y*D}; } inline double mod (const Point &A) return A.x*A.x+A.y*A.y; } inline double pf (double x) return x*x; } inline double dis (const Point &A,const Point &B) return sqrt (pf (A.x-B.x)+pf (A.y-B.y)); } inline bool operator < (const Point &A,const Point &B){ if (abs ((A-p0)*(B-p0))>eps) return ((A-p0)*(B-p0))>eps; else return dis (p0,A)<dis (p0,B); } Point stk[MAXN]; int top,cnt;inline void Insert (Point a) p[++cnt]=a; if (p[pos].y>p[cnt].y||(p[pos].y==p[cnt].y&&p[pos].x>p[cnt].x)) pos=cnt; } inline int Next (int x) return (x>=top?x-top+1 :x+1 ); } Point Ans[4 ]; int main () int n; scanf ("%d" ,&n); pos=1 ; for (register int i=1 ;i<=n;++i){ double x,y; scanf ("%lf%lf" ,&x,&y); Insert (Point{x,y}); } p0=p[pos]; swap (p[1 ],p[pos]); sort (p+2 ,p+1 +cnt); for (register int i=1 ;i<=cnt;++i){ while (top>1 &&(stk[top]-stk[top-1 ])*(p[i]-stk[top-1 ])<=0 ) top--; stk[++top]=p[i]; } double ans=1e20 ; stk[top+1 ]=stk[1 ]; int l=2 ,r=2 ,h=2 ; Point ansl1,ansr1,ansl2,ansr2; for (register int i=1 ;i<=top;++i){ while (((stk[h]-stk[i])*(stk[i]-stk[i+1 ]))<((stk[Next (h)]-stk[i])*(stk[i]-stk[i+1 ]))+eps) h=Next (h); while (((stk[r]-stk[i])^(stk[i]-stk[i+1 ]))+eps>((stk[Next (r)]-stk[i])^(stk[i]-stk[i+1 ]))) r=Next (r); if (i==1 ) l=r; while (((stk[l]-stk[i])^(stk[i]-stk[i+1 ]))<((stk[Next (l)]-stk[i])^(stk[i]-stk[i+1 ]))+eps) l=Next (l); double D=dis (stk[i],stk[i+1 ]); double H=abs ((stk[h]-stk[i])*(stk[i]-stk[i+1 ]))/D; double L=abs ((stk[l]-stk[i])^(stk[i]-stk[i+1 ]))/D; double R=abs ((stk[r]-stk[i])^(stk[i]-stk[i+1 ]))/D; if (ans>H*(L+R)){ ans=H*(L+R); Point a=stk[i]-stk[h],b=stk[i+1 ]-stk[h]; double aa=mod (a),bb=mod (b); double x=sqrt (abs (aa-H*H)),y=sqrt (abs (bb-H*H)); Point hh=(mul (a,y)+mul (b,x))/(x+y); Point jzm=stk[i+1 ]-stk[i]; if (abs (D)>=eps) ansl1=stk[i]+mul (jzm,-L/D); else ansl1=stk[i]; if (abs (D)>=eps) ansr1=stk[i]+mul (jzm,R/D); else ansr1=stk[i]; ansl2=ansl1-hh; ansr2=ansr1-hh; } } PrintDouble (ans); printf ("\n" ); p0=Point{0 ,0 }; Ans[0 ]=ansl1,Ans[1 ]=ansl2,Ans[2 ]=ansr1,Ans[3 ]=ansr2; sort (Ans,Ans+4 ); Ans[0 ].print (); Ans[1 ].print (); Ans[2 ].print (); Ans[3 ].print (); }
三维凸包:咕咕咕