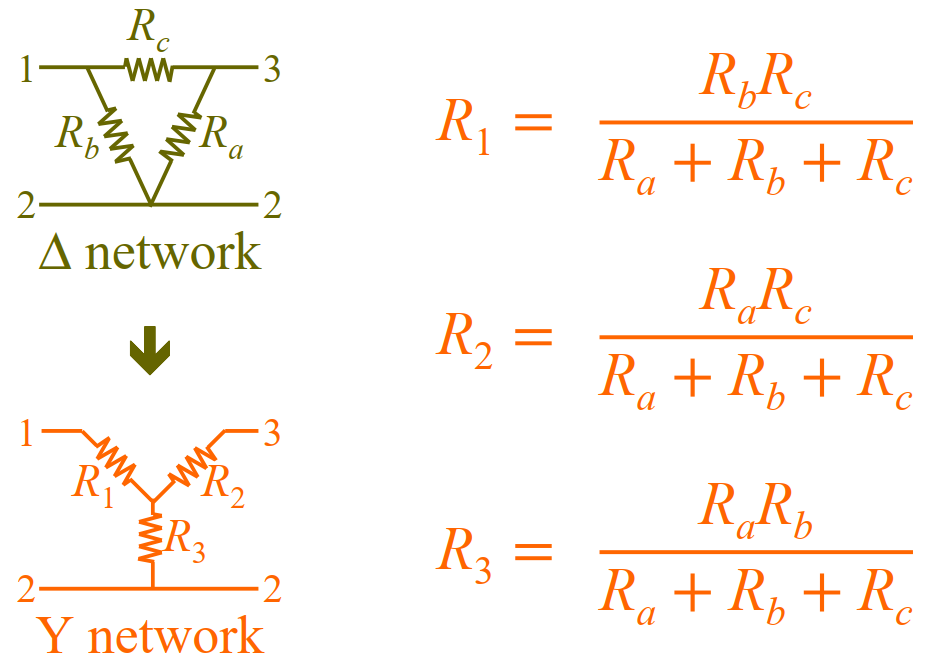
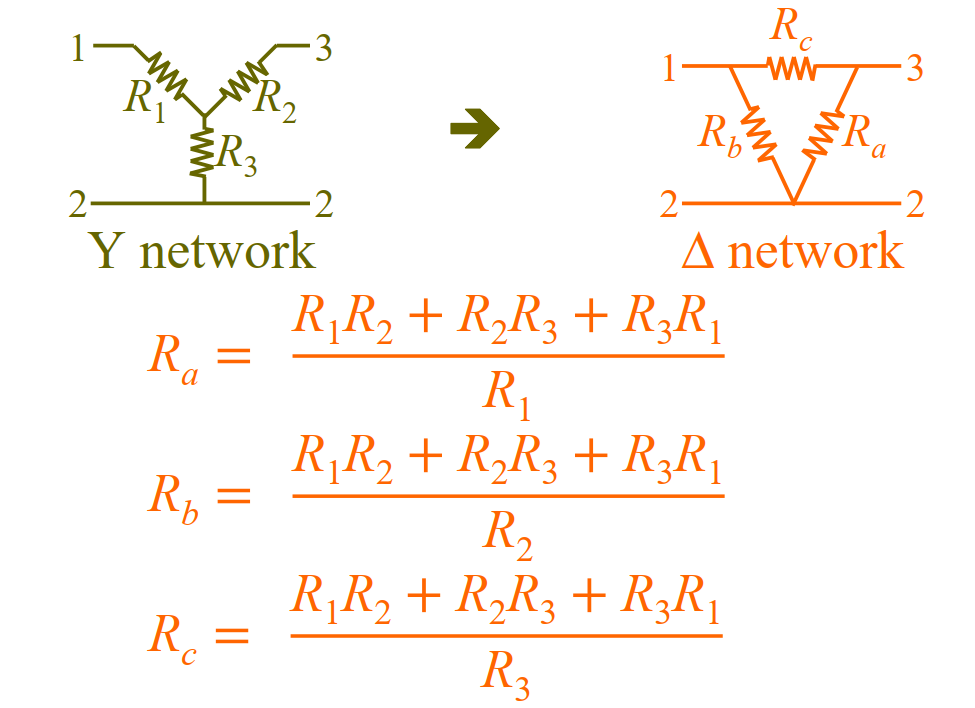
P38.
resistor 电阻
resistance 电阻值
resistivity 电阻率
conductor 电导
conductance 电导值
conductivity 电导率
series (combination / connection) 串联
parallel (combination / connection)并联
network topology网络拓扑
branch支路
node结点
loop 回路
成比例的 proportional
infinity 无穷大
reciprocal 倒数
slope 斜率
numerator 分子
denominator 分母
Introduction
The materials physical property of resisting current flow is represented by resistance R, measured in ohms (Ω).
Ohm’s Law

Ohm’s Law .
Linear and nonlinear resistors.
Fixed and variable resistor.
An element’s physical property of resisting electric current, measured in ohms (Ω).
An element’s ability of conducting electric current, measured in mhos or siemens (S).
Good habit: labeling current direction and voltage polarities following PSC.
When reference direction of current and voltage are not given,
- Indicate passive elements following PSC.
- Indicate active elements following ASC.
Two circuits are said to be equivalent if they have same - or - relationship at a pair of terminals.
Nodes, Branches, and Loops 节点、支路和回路
A network: an interconnection of elements or devices.
A circuit: a network providing one or more closed paths.
Network (circuit) topology: studying properties relating to the elements placement and the geometric configuration.
A branch represents any two-terminal element.
A node is point of connection between two or more branches.
A loop is any closed path in a circuit without passing through any node more than once.
An independent loop contains at least one branch that is not a part of any other independent loop.
-
: Number of independent loops
-
: Number of branches
-
: Number of nodes
Number of independent loops indicates number of independent sets of KVL Eqs.
In circuit analysis, we write Eqs. for nodes’ voltage and branches’ current.
Kirchhoff’s Laws
KCL
Based on law of conservation of charge, it states that algebraic sum of currents entering a node (or a closed boundary) is zero.
KCL — Alternative form
Sum of currents entering a node is equal to sum of currents leaving the node.
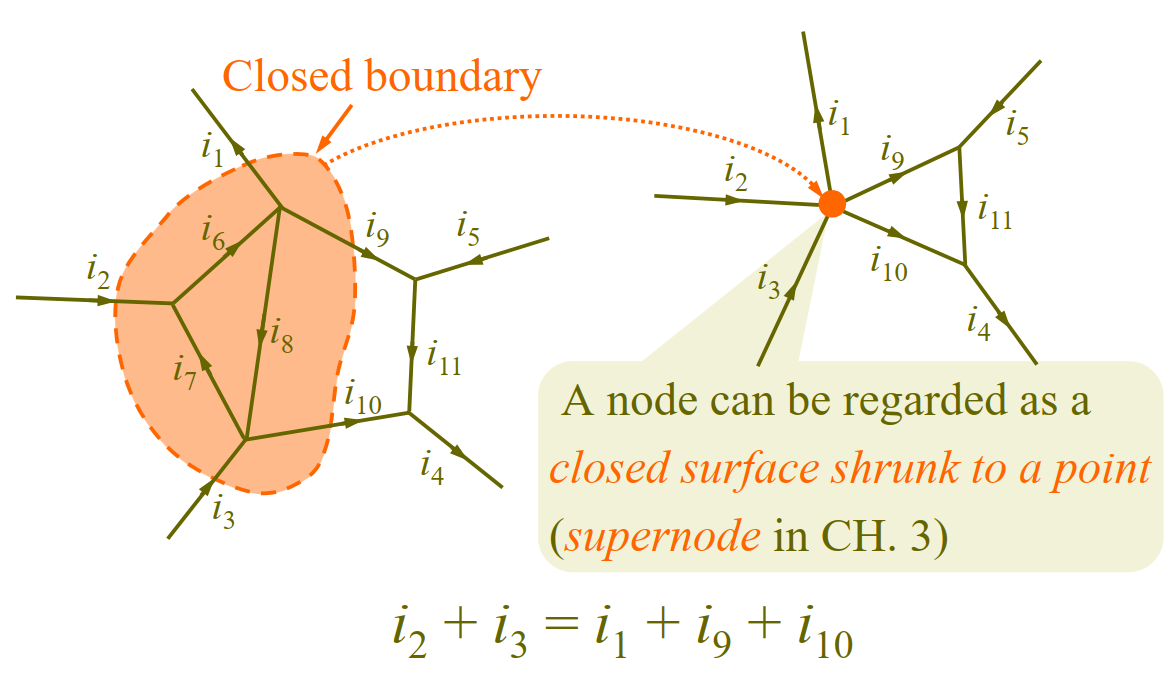
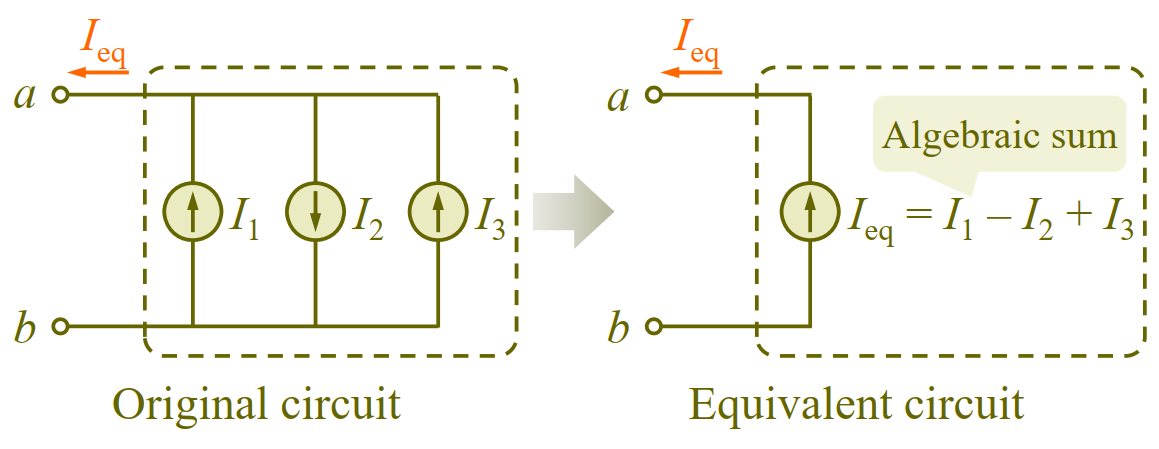
Application of KCL: combining current sources in parallel.
A circuit cannot contain two different currents in series unless they are same.
KVL
Based on law of conservation of energy, it states that algebraic sum of voltages around a closed path (or a loop) is zero.
: Number of voltages (branches) in a loop
: th voltage
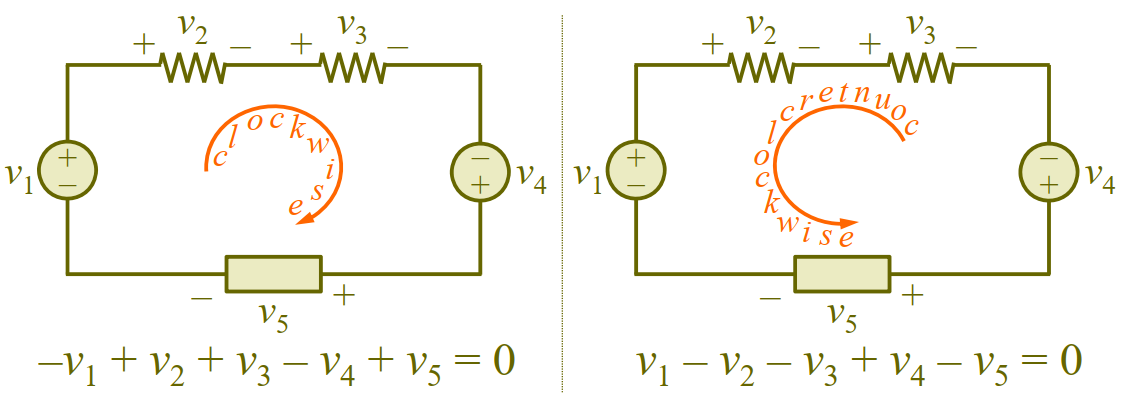
-
Start with any branch and go around loop either clockwise or counterclockwise
-
Sign on each voltage is polarity of terminal encountered first as travelling around loop
For an -node -branch circuit, there are independent KVL Eqs.
Simplify circuit as possible as you can before using any methods.
Series Resistors and Voltage Division
Principle of voltage division: source voltage is divided among resistors in direct proportion to their resistances, which means the larger the resistance, the larger the voltage drop.