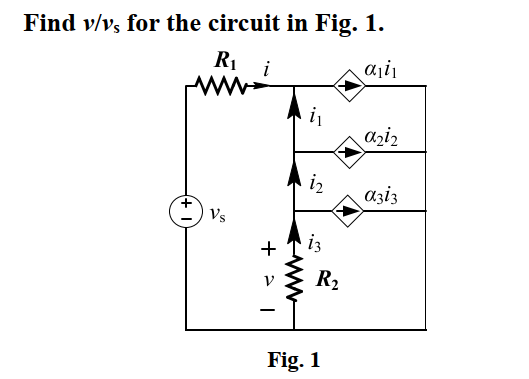
Introduction

Kirchhoff’s Current & Voltage Law
-node -branch circuit:
- independent KCL Eqs.
- independent KVL Eqs.
Nodal Analysis
Goal: Finding Node Voltages.
Assumption: Circuits Having no voltage source.

- Selecting reference node and assigning voltages to remaining nodes. 非参考节点的个数等于独立方程的个数。
- Common ground
- Ground
- Chassis ground (基座)
- Applying KCL to each nonreference nodes and expressing in terms of .
- Element Voltage
- PSC: . 通过电阻的电流总是从高电位向低电位流动。认为电流方向的起始点为高电位,电流方向的终止点为低电位。
- Solve Eqs. by Substitution method, Elimination method, Cramer’s rule, Matrix inversion.
- Solving simultaneous Eqs. to obtain unknown voltages.
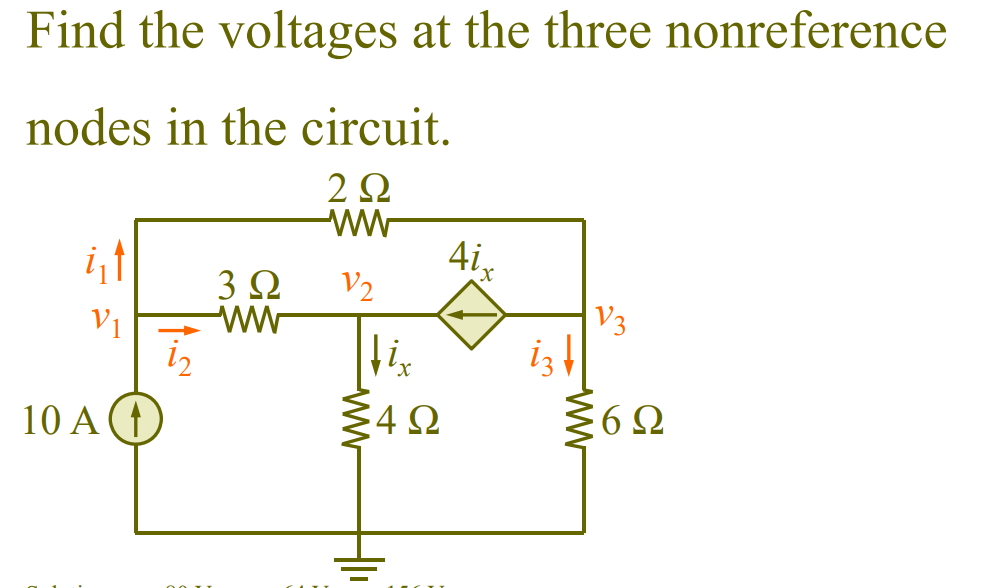
Nodal Analysis with Voltage Sources
Case 1
Voltage source connected between reference node and non reference node
Case 2
Independent or dependent voltage source connected between two nonreference nodes.
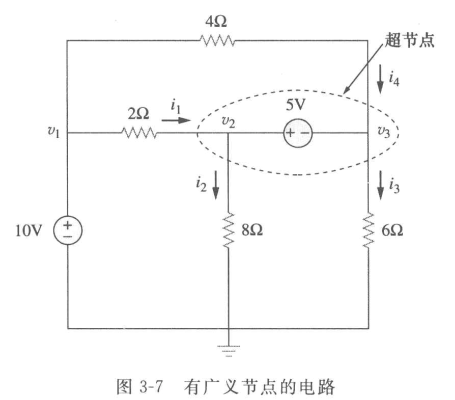
Forming a supernode.
Introduced because the current through voltage source is unknown. “缩边、缩点”
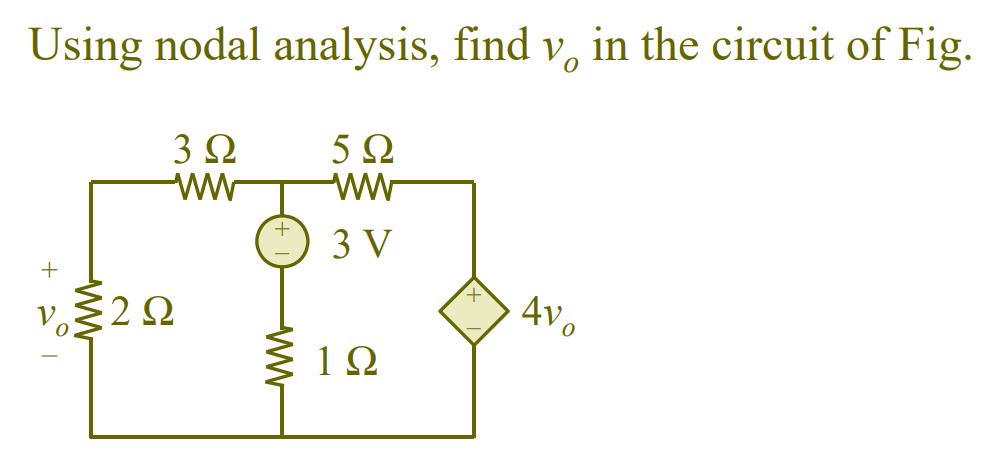
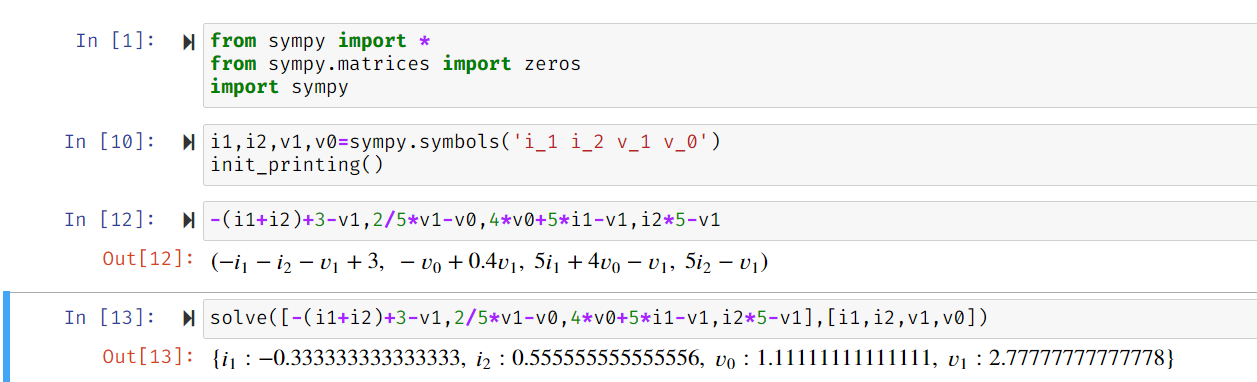
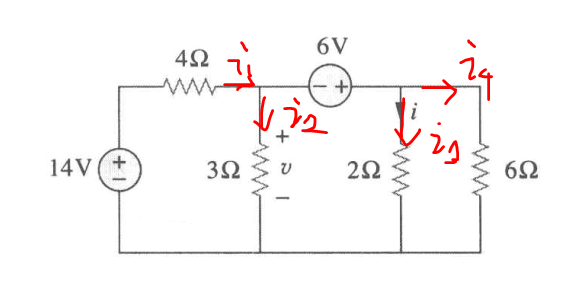
.
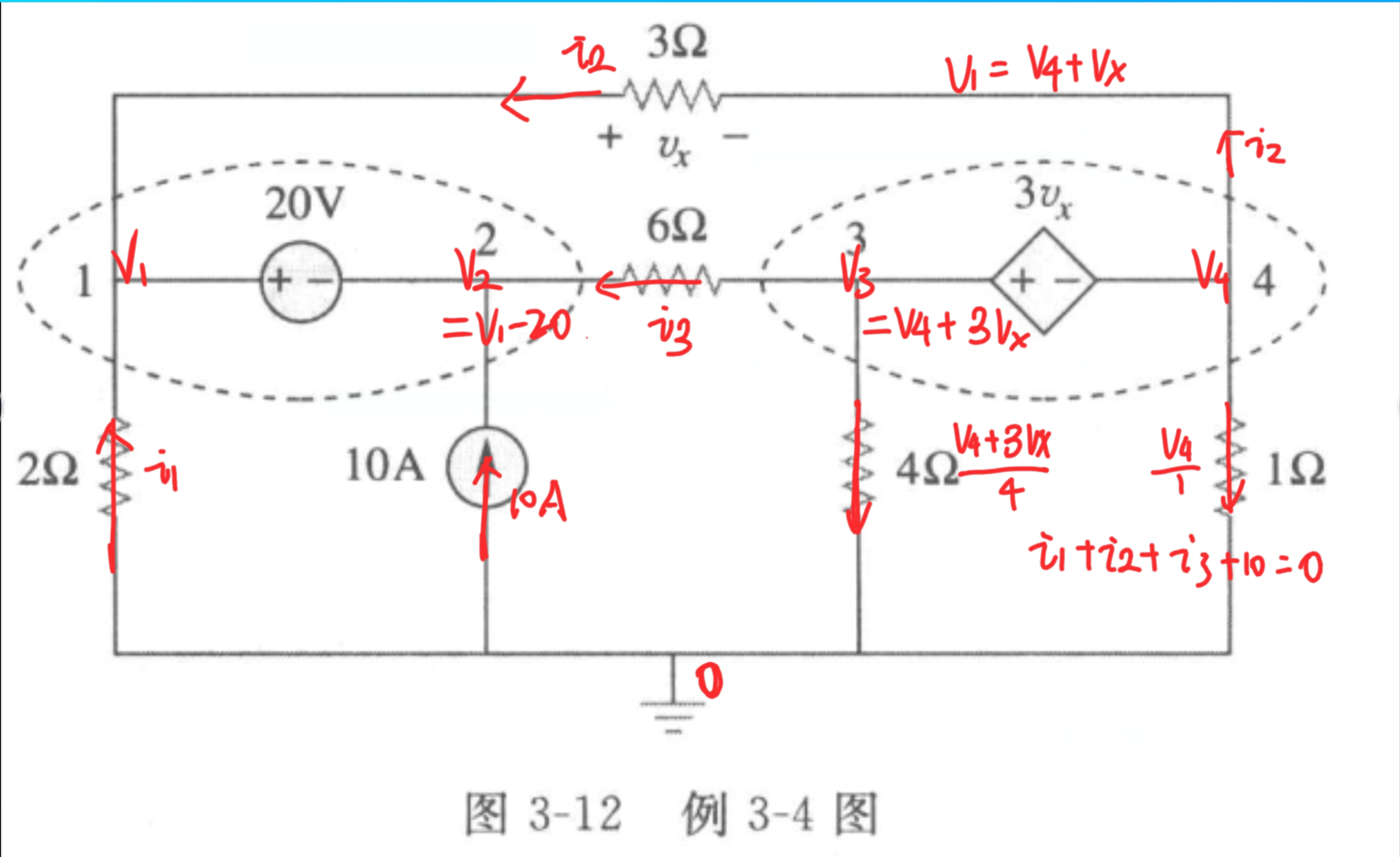
Mesh Analysis
- A loop: a closed path with no node passed more than once.
- A mesh: a loop that does not contain any other loops within it.
Planar circuit.
- Assign mesh currents to meshes.
- Applying KVL to each mesh and expressing voltages in terms of mesh currents. (Nodal: voltage $\to $ current)
- Solving simultaneous Eqs to obtain unknown currents.


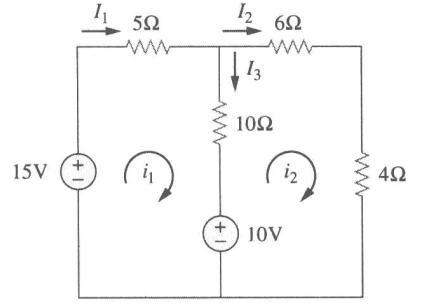
电流方向符合 ASC,等号另一边就是正的。
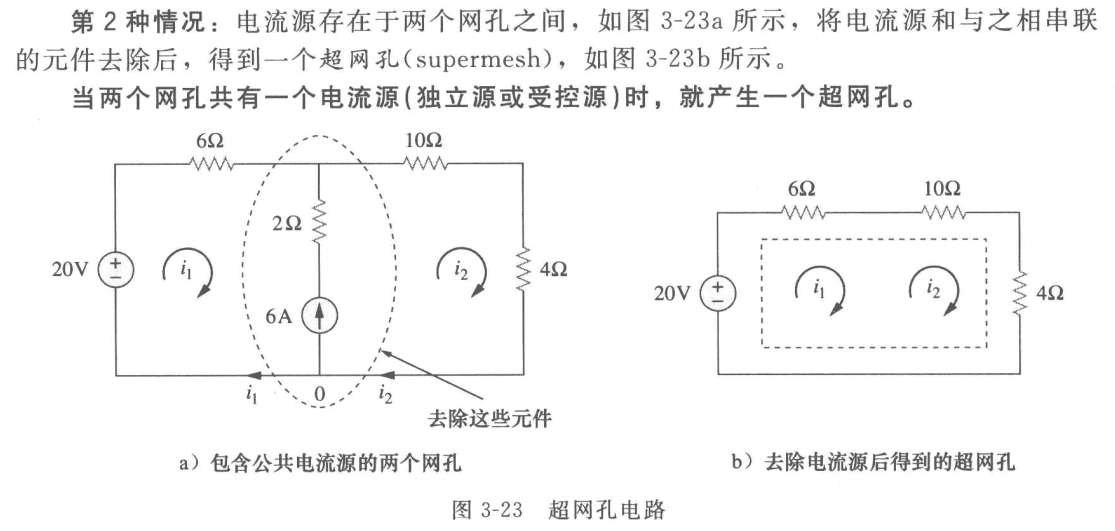
Mesh Analysis with Current Sources
-
Only in one mesh.
-
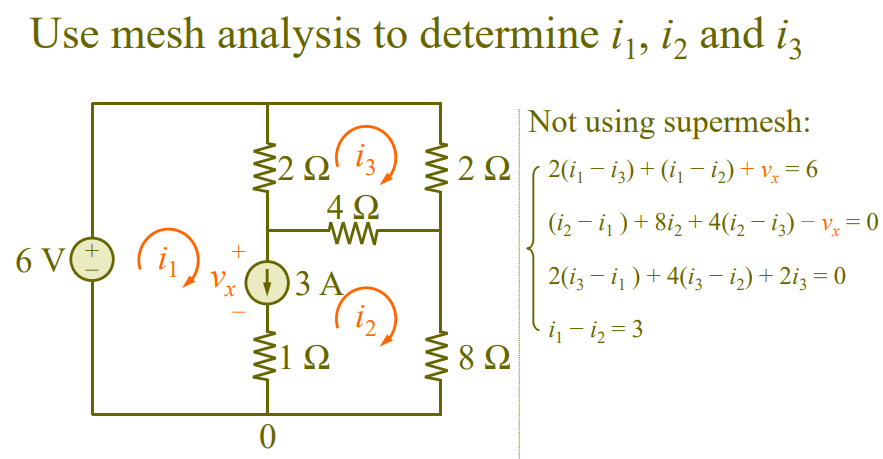
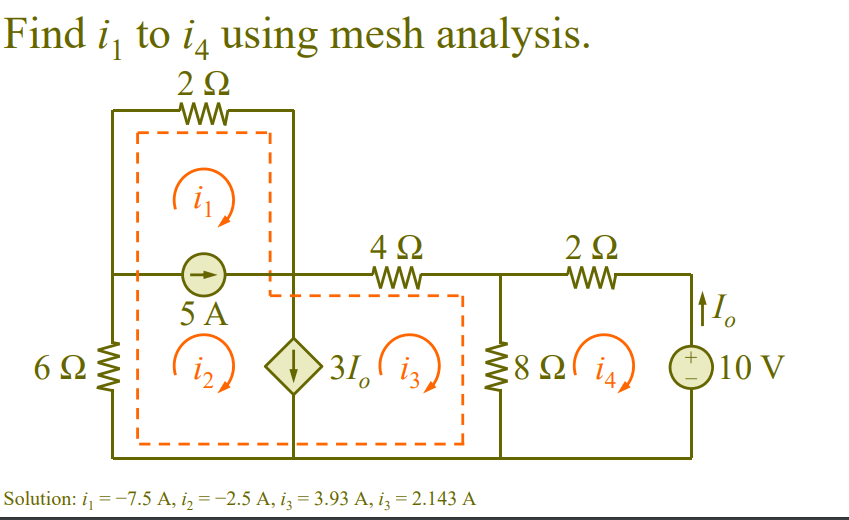
Between two meshes. Supermesh. Voltage across current source is not known. Formed by excluding current source and any elements connected in series with it.
Current Sources have corresponding voltages.
Assume additional voltages.

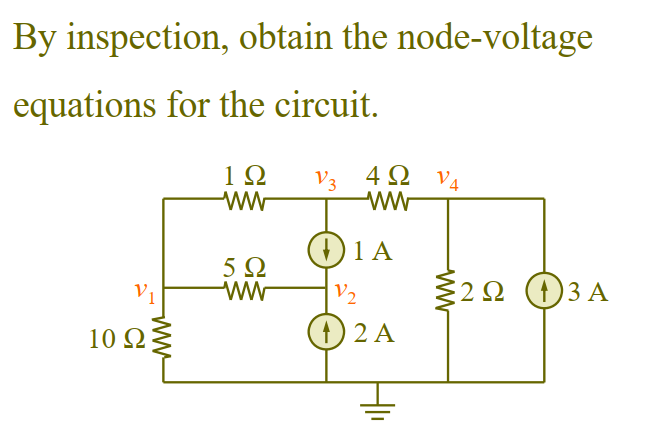
Nodal Analyses by Inspection
取进入节点为正值

Sum of conductances directly connected to node
: Negative of sum of conductances directly connecting nodes and .
Unknown voltage at node
: Sum of all independent current sources directly connected to node , with currents entering node treated as positive
This is valid for circuits with only independent current sources and linear resistors.


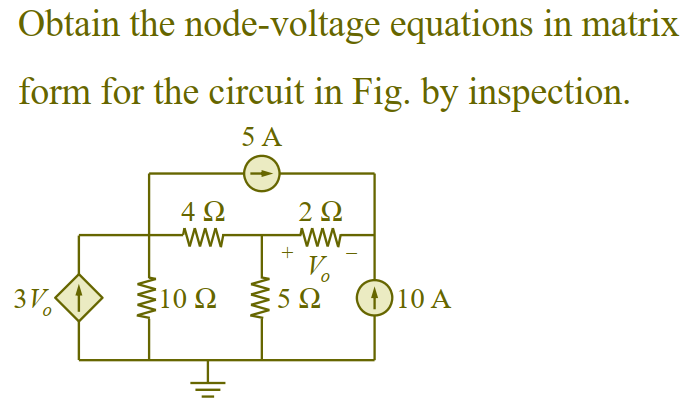

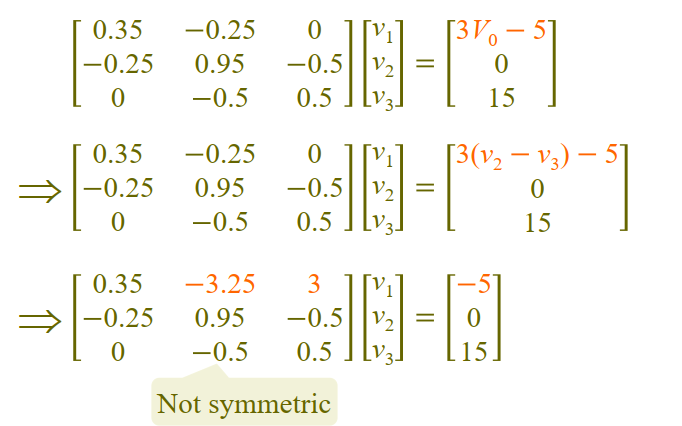
Mesh Analyses by inspection
和网孔分析法一样,取ASC方向的电源为正值。

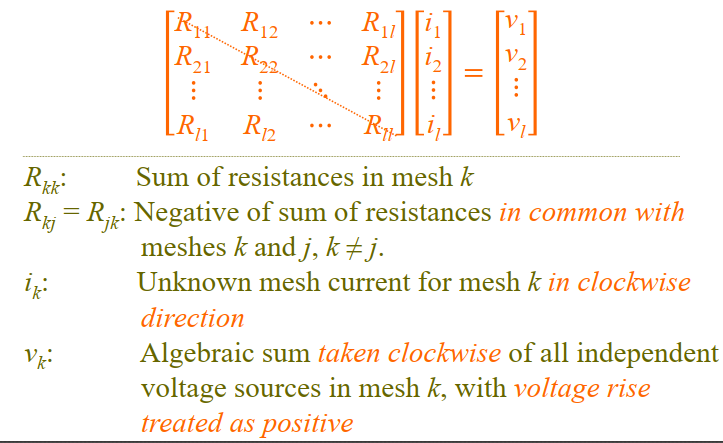
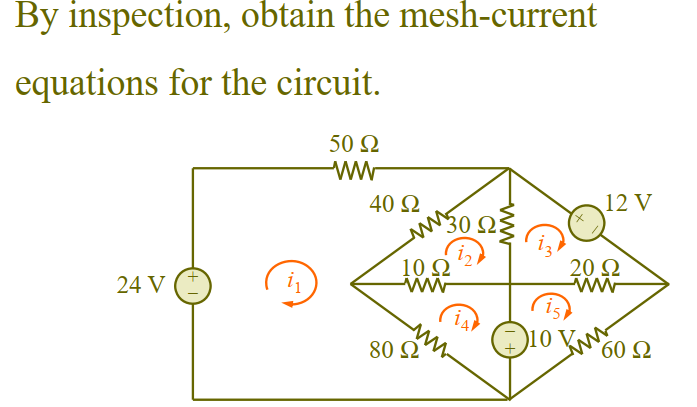


Problems
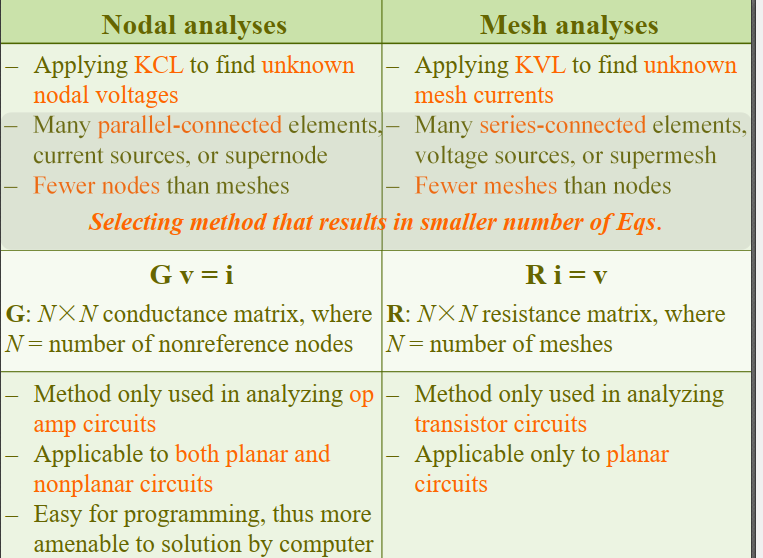
Chapter 3, Problem 40.

Assume all currents are in and apply mesh analysis for mesh 1.
for mesh 2,
for mesh 3,
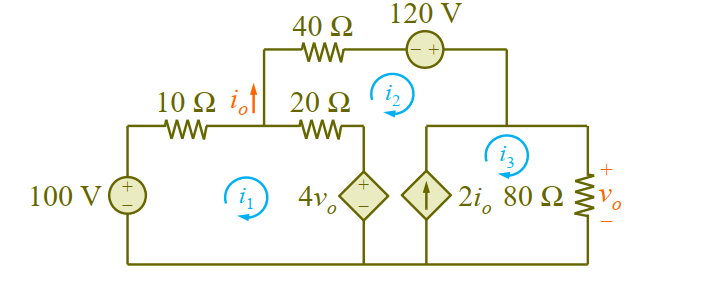
Chapter 3, Problem 41.
Apply mesh analysis to find in Fig. 3.87.

For loop 1,
For loop 2,
For loop 3,
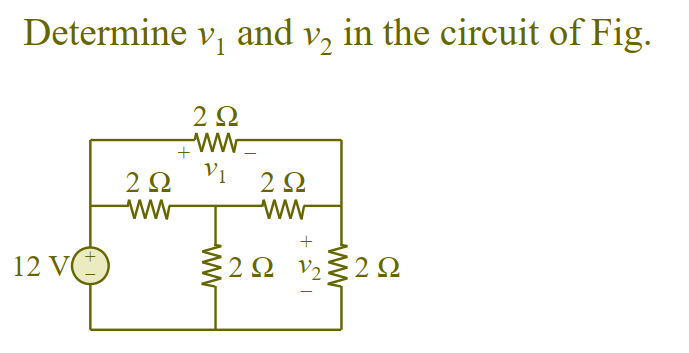
Chapter 3, Problem 44.
Using Super Mesh

Loop 1 and 2 form a supermesh. For the supermesh. (We assume and , the total number of variables assumed in supermesh is equal to ordinary mesh analysis, however, we consider the corresponding current with respect to each branch)
For loop 3,
Chapter 3, Solution 45.

Chapter 3, Solution 46.

Chapter 3, Problem 51.

We can only tell that equals to 5A because the voltage across the current source is unknown.
Chapter 3, Problem 60.

At node 1,
At node 2,
Chapter 3, Problem 62.
Find the mesh currents and in the network of Fig. 3.106.

Supermesh
Chapter 3, Problem 63.


Chapter 3, Problem 64.

Using Super Mesh. Excluding current sources.

We don’t have to assume ^ this mesh current, because there are no passive elements on this mesh.
For the super mesh,
For the smaller mesh,
Now we have 2 equations for 4 unknowns, so we need 2 extra equations.
For the first equation, use KCL,
For the second equation, see B as a node.
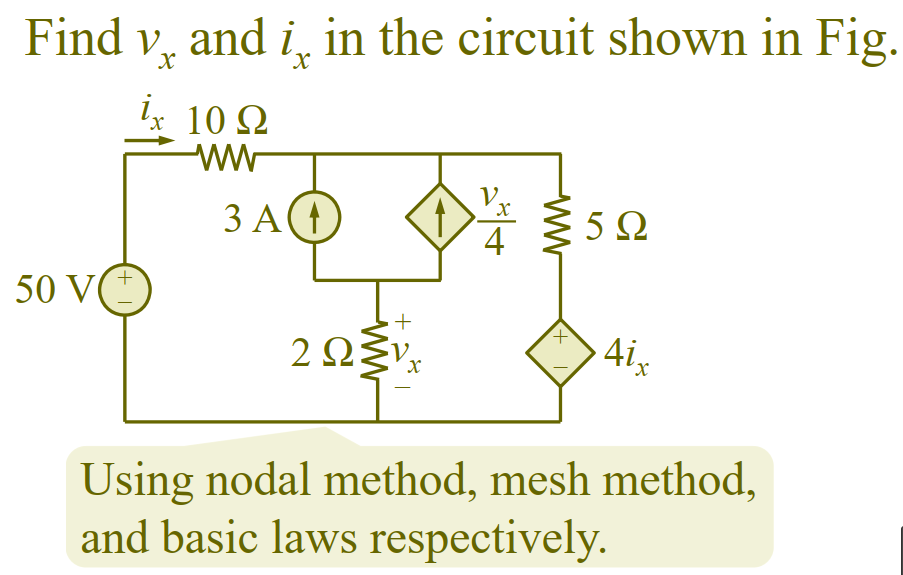
Chapter 3, Problem 67


代回原式即可解。
Chapter 3, Problem 73.